1.IPCONFIG: IP Configuration
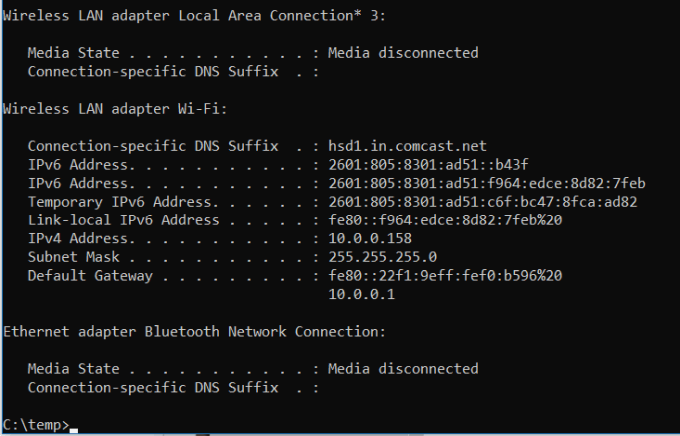
Network troubleshooting is never simple, but one command that makes it much easier is IPCONFIG.
Using this command in the CMD command prompt returns detailed information about your current network adapter connection including:
- Current IP Address
- Subnet Mask
- Default Gateway IP
- Current domain
This information can help you troubleshoot router issues and other connection issues you could be having with your network adapter.
2.NETSTAT: Network Statistics
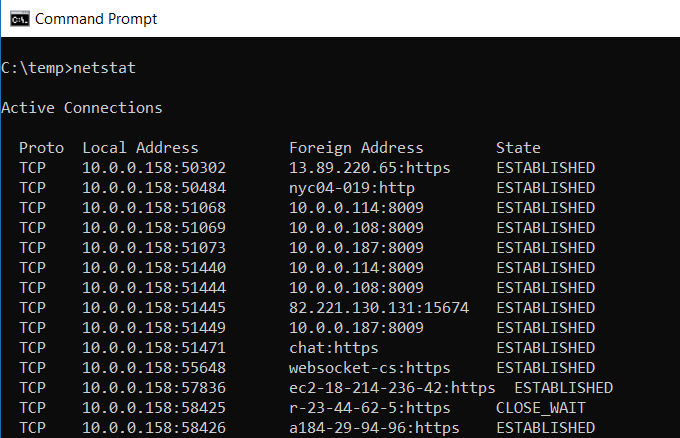
Concerned that you could have malware running on your computer that’s connecting to internet locations without you knowing about it?
If you run a NETSTAT command in the command prompt, you can get a list of all active TCP connections from your computer.
3. PING: Send Test Packets
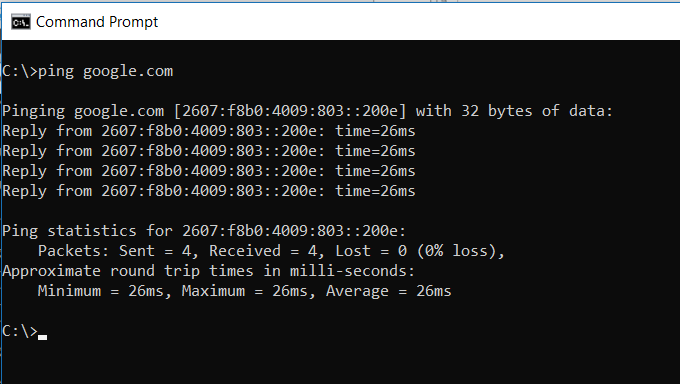
An IT Analyst’s best friend is the PING command. Running this command sends test packets over the network to the target system.
You can use the PING command to test whether your computer can access another computer, a server, or even a website. It can help with revealing network disconnections. It also provides transit time for the packets in milliseconds, so it also reveals a bad network connection as well.
4. TRACERT: Trace Route
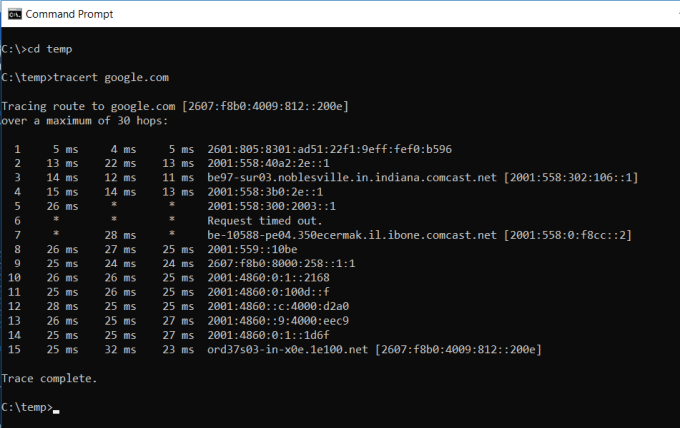
TRACERT is a fascinating Windows Command to use. If you’re ever curious to see the path your internet traffic takes to get from your browser to a remote system like Google servers, you can use TRACERT to see it.
The command stands for “Trace Route”, which sends packets out to a remote destination (server or website), and provides you with all of the following information:
- Number of hops (intermediate servers) before getting to the destination
- Time it takes to get to each hop
- The IP and sometimes the name of each hop
TRACERT can reveal how the routes of your internet requests change depending where you’re accessing the web. It also helps with troubleshooting a router or switch on a local network that may be problematic.
5. POWERCFG: Power Configuration
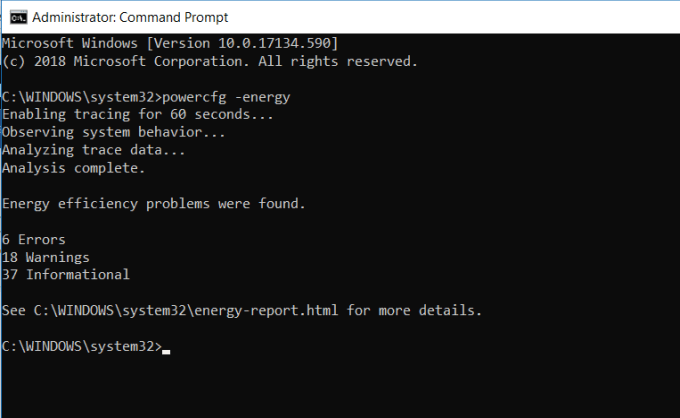
Are you frustrated with how quickly your laptop seems to run out of power? It could be that your power settings are configured as efficiently as possible. There’s a windows CMD command called POWERCFG (power configuration) that can help. Run the command prompt as an administrator and type powercfg – energy to get a full power efficiency report.
The process can take up to about a minute, but when it’s done, you’ll see whether there are any warnings or errors that might help you improve the power efficiency of your system.
ils of those errors and warnings.
6. SHUTDOWN: Turn Off Computer
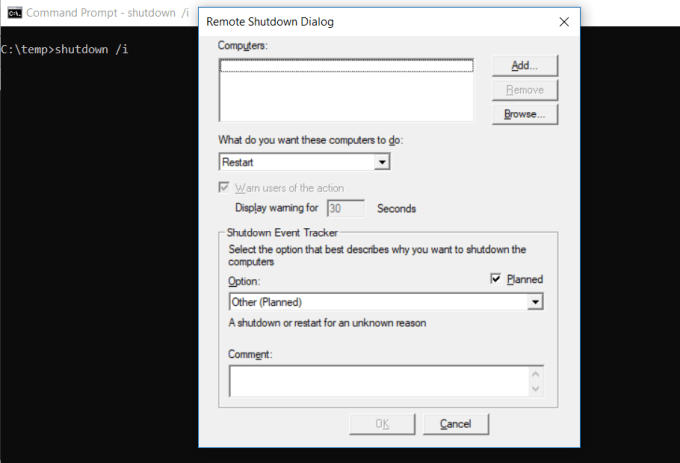
The SHUTDOWN command is a pretty versatile command that lets you shutdown the computer but control the behavior of that shutdown. It’s commonly used as a scheduled task or part of an IT batch job after patches have been applied to a computer system.
Typing shutdown /i from the command prompt will initiate a shutdown, but it’ll upon a GUI to give the user an option on whether to restart or do a full shutdown. If you don’t want to have any GUI pop up, you can just issue a shutdown /s command.
There is a long list of other parameters you can use to do a log off, hibernate, restart, and more. Just type shutdown without any arguments to see them all.
7. SYSTEMINFO: System Information
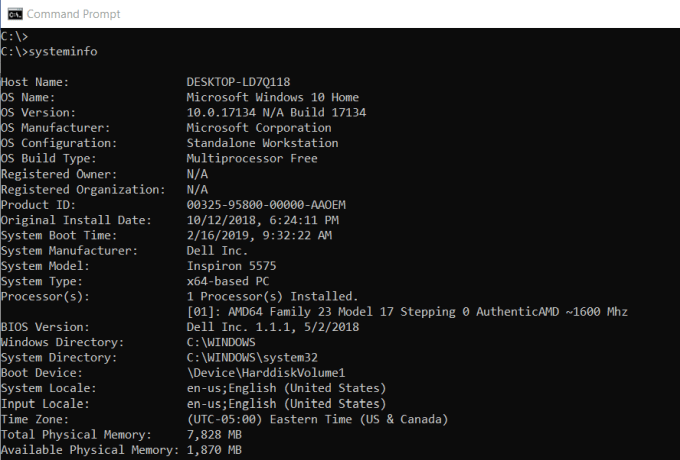
If you need to know what brand of network card you have, processor details, or the exact version of your Windows OS, the SYSTEMINFO command can help.
This command polls your system and pulls the most important information about your system. It lists the information in a clean format that’s easy to read.
8. SFC: System File Checker
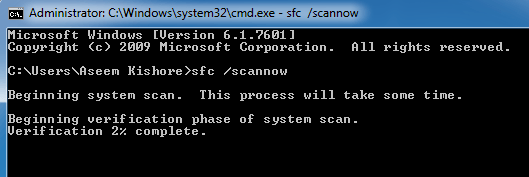
If you’re ever concerned that a virus or some other software might have corrupted your core system files, there’s a Windows command that can scan those files and ensure their integrity.
You need to launch CMD as administrator (right click and choose Run as Administrator). Typing SFC /SCANNOW will check the integrity of all protected system files. If a problem is found, the files will be repaired with backed-up system files.
The SFC command also lets you:
- /VERIFYONLY: Check the integrity but don’t repair the files.
- /SCANFILE: Scan the integrity of specific files and fix if corrupted.
- /VERIFYFILE: Verify the integrity of specific files but don’t repair them.
- /OFFBOOTDIR: Use this to do repairs on an offline boot directory.
- /OFFWINDIR: Use this to do repairs on an offline Windows directory.
- /OFFLOGFILE: Specify a path to save a log file with scan results.
The scan can take up to 10 or 15 minutes, so give it time.
9. NET USE: Map drives
If you want to map a new drive, you could always open File Explorer, right click on This PC, and go through the Map Network Drive wizard. However, using the NET USE command, you can do the same thing with one command string.
For example, if you have a share folder on a computer on your network called \\OTHER-COMPUTER\SHARE\, you can map this as your own Z: drive by typing the command:
Net use Z: “\\OTHER-COMPUTER\SHARE” /persistent:yes
The persistent switch tells your computer that you want this drive remapped every time you log back into your computer.
10. CHKDSK: Check Disk
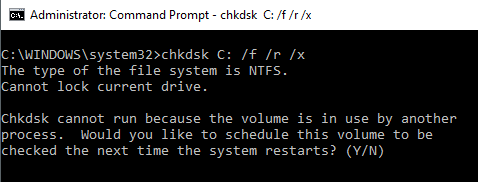
While the SFC command only checks the integrity of core system files, you can use the CHKDSK command to scan an entire drive.
The command to check the C: drive and repair any problems, launch the command window as an administrator and type CHKDSK /f C:.
This command checks for things like:
- File fragmentation
- Disk errors
- Bad sectors
The command can fix any disk errors (if possible). When the command is finished, you’ll see a status of the scan and what actions were taken.
11. SCHTASKS: Schedule Tasks
Windows comes with a wizard for creating scheduled tasks. For example, maybe you have a BAT file stored on C:\temp that you want to run every day at noon.
You’d have to click through the Scheduled Task wizard to configure this. Or you can type a single SCHTASKS command to set it up.
SCHTASKS /Create /SC HOURLY /MO 12 /TR Example /TN c:\temp\File1.bat
The scheduled switch accepts arguments like minute, hourly, daily, and monthly. Then you specify the frequency with the /MO command.
If you typed the command correctly, you’ll see the response, SUCCESS: The scheduled task “Example” has successfully been created.
12. ATTRIB: Change File Attributes
In Windows, you can change file attributes by right clicking on a file and finding the right property to change. However, instead of hunting around for the file attribute, you can use the ATTRIB command to set the file attributes.
For example, if you type: ATTRIB +R +H C:\temp\File1.bat, it’ll set File1.bat as a hidden, read-only file.
There is no response when it’s successful, so unless you see an error message, the command worked.
